Now you do need a free tier OCI account and upgrade it to a Pay as you go (PAYG) account due to the NAT not being included in the free tier.
I do recommend setting up a budget in the Billing & Cost Management->Cost Management->Budgets.
Setting up a new budget with the minimun value lets you track if anything goes wrong in your deployment and you can avoid paying anything!

Now we can start to setup our cluster!
-
Head on to
Kubernetes Clusters (OKE)andCreate cluster. -
Click on
Quick create. -
Use a
Public endpointso that we can expose your cluster to the internet. -
Select
Node typeasManagedso that we can ony use our free tier resources and not incur any costs. -
In
Shape and imageselectVM.Standard.A1.Flexand you can choose the shape as:- 1 OCPU and 6 GB Memory and 4 Node count.
- 2 OCPU and 12 GB Memory and 2 Node count.
-
By default the boot size is 46.6 GB, you can increase this to 50 GB in the advanced options to fully use the 200 GB free tier storage.
-
Select next and be sure to select the
Create a Basic clusteras the Enhanced cluster incur costs each day.
It will take around 10 mins for all your nodes to come online in the nodepool and then your free kubernetes cluster will be active!
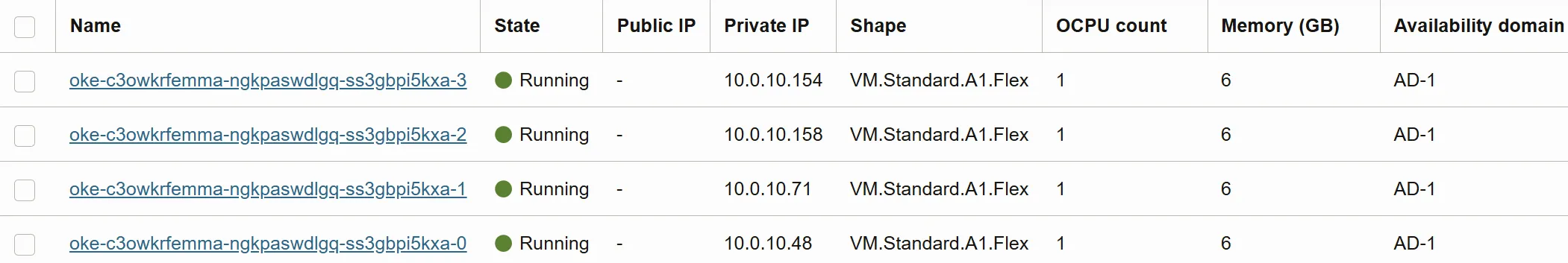
You can also check your cluster nodes in the Instances section:
Now you do need to install OCI on your laptop to access your cluster.
- You need to first run this command and use the defaults or whatever parameters you want
bash -c "$(curl -L https://raw.githubusercontent.com/oracle/oci-cli/master/scripts/install/install.sh)"
-
You do need to configure your OCI setup, follow the link for more instructions. Quickstart (oracle.com)
-
Once done, you can access your cluster using the command provided in your OCI console It should look like this
oci ce cluster create-kubeconfig --cluster-id ocid1.cluster.oc1.ap-mumbai-1.aaaaa --file $HOME/.kube/config --region ap-mumbai-1 --token-version 2.0.0 --kube-endpoint PUBLIC_ENDPOINT
- Now you need to export the KUBECONFIG to enable your kubectl use the configs
export KUBECONFIG=$HOME/.kube/config
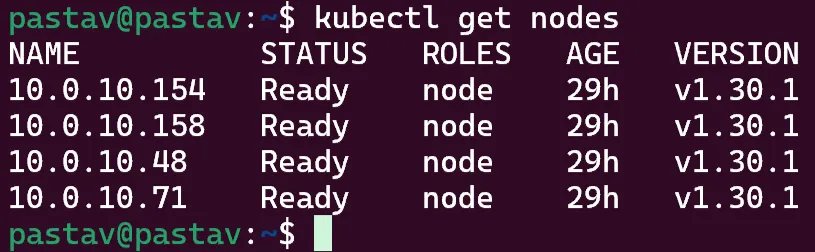
Now you can check your nodes!
kubectl get nodes